A river having its head stream in a devastated mountain is prone to the aggradation of a riverbed due to the deposit of sediments flowing from the mountain, thereby causing floods and damages through the entire river basin. In such a river it is necessary to control sediment runoff from the upper stream and prevent extreme changes in the height of the downstream riverbed (Fig. 1). Sabo works for such purpose is called “River System Sabo”
Collapsed Land Areas in Japan




Sabo Works on Mt. Tateyama Protecting the Toyama Plain

Fig1.
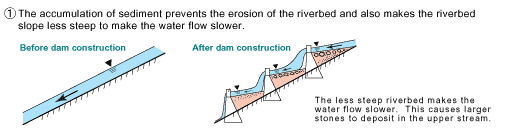
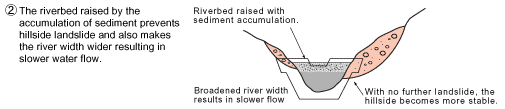
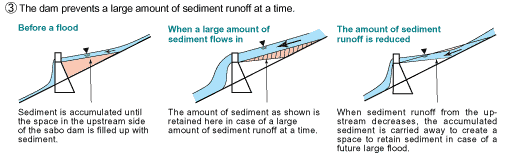
Fig. 1) A sabo dam prevents riverbed erosion, hillside landslide and a large amount of sediment flow at a time by accumulating sediment in it.
Fig. 2
Joganji River is at such a high altitude at a 10km-point from its river mouth that Toyama City can be viewed down below from that point. On top of this, Joganji River is a raised bed river.
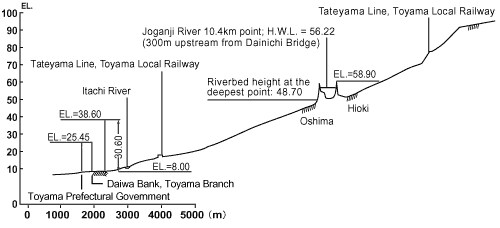
Fig.2) Joganji River is at such a high altitude at a 10kmpoint from its river mouth located on the alluvial fan in the Toyama Plain that Toyama City can be viewed down below from that point. On top of this, Joganji River is a raised bed river. A raised bed river is a river whose riverbed is raised above the surrounding ground due to sediment deposit inside the river banks. A large amount of sediment flow from the upstream has raised the riverbed of Joganji River above the ground over a long period. Once it floods, it may cause a severe disaster.